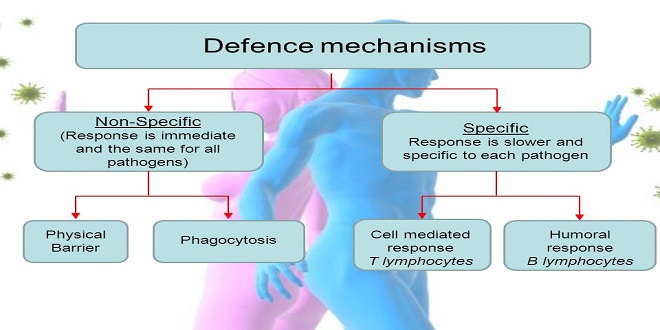
Viruses as Human Pathogen DNA Viruses Viruses with Single-Stranded DNA Genomes
The groups of viruses with single-stranded DNA genomes are contained in only one family, the parvoviruses, with only a single human pathogen type. The Geminiviridae, Circoviridae, and many other families have circular single-stranded DNA but infect only plants and, more rarely, animals.
Parvoviruses
This group’s only human pathogen, parvovirus B19, is the causative virus in erythema infectiosum (also known as “slapped cheek syndrome” or the “fifth disease”) in children and causes an aplastic crisis in anemic patients. The virus also contributes to joint diseases, embryopathies, and tissue rejection following renal transplants. Diagnosis: serological (IgG and IgM) and PCR.
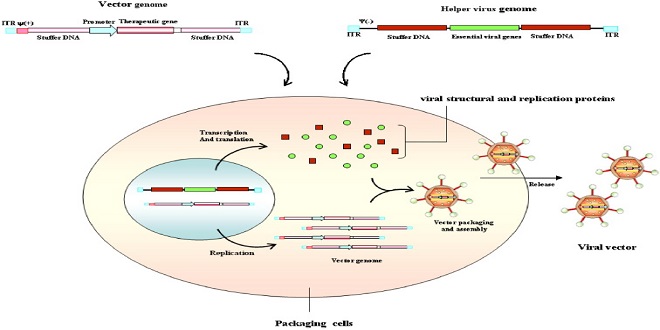
The parvoviruses are among the smallest viruses with a diameter of 19–25 mm. They are icosahedral and nonenveloped, and their genome is in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Some parvoviruses can only replicate in the presence of a helper virus (adenovirus or herpesvirus). health
Parvovirus B19, the only human pathogenic parvovirus identified to date, is capable of autonomic replication, i.e., it requires no helper virus. Some zoopathic strains also show this capability in rodents, dogs, and pigs.
The parvoviruses are among the smallest viruses with a diameter of 19–25 mm. They are icosahedral and nonenveloped, and their genome is in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Some parvoviruses can only replicate in the presence of a helper virus (adenovirus or herpesvirus). Parvovirus B19, the only human pathogenic parvovirus identified to date, is capable of autonomic replication, i.e., it requires no helper virus. Some zoopathic strains also show this capability in rodents, dogs, and pigs
sum (“slapped-cheek syndrome” or “fifth disease”). This childhood disease, which used to be classified as atypical measles, is characterized by sudden onset of exanthem on the face and extremities. Certain forms of arthritis are considered complications of a parvovirus B19 infection. The virus also appears to cause spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy and fetal damage in late pregnancy (hydrops fetalis).
. An enzyme immunoassay reveals antibodies of the IgG and IgM classes. During the viremic phase, at the onset of clinical symptoms, the virus can also be identified in the blood by means of electron microscopy or PCR. In-vitro culturing of the pathogen is not standard procedure. Epidemiology and prevention.
The transmission route of human parvovirus B19 is not known. Droplet infection or the fecal-oral route, analogous to other parvoviruses, is suspected. Blood and blood products are infectious, so multiple transfusion patients and drug addicts are high incidence groups. No specific prophylactic measures are recommended.
Viruses with Double-Stranded DNA Genomes
Viruses with double-stranded DNA genomes are classified in six families: papillomavirus, polyomavirus, adenovirus, herpesvirus, poxvirus, and hepadnavirus. Carcinogenic types have been found in all groups except the poxviruses (see Chapter 7, DNA tumor viruses).
Papillomaviruses
The over 70 viral types in the genus Papillomavirus are all involved in the etiology of benign tumors such as warts and papillomas, as well as malignancies, the latter mainly in the genital area (cervical carcinoma). These organisms cannot be grown in cultures. Diagnosis therefore involves direct detection of the viral genome and histological analysis. Serology is less important in this group.
Last word
The papillomaviruses have a diameter of 55 nm and contain an 8 kbp dsDNA genome. There are two distinct regions within the circular genome: one that codes for the regulator proteins produced early in the replication cycle and another that codes for the structural proteins synthesized later.